The International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)2 offers CAP certification to those professionals who want to demonstrate their skills and expertise in authorizing and maintaining information systems tasks within Risk Management Framework (RMF). Initially developed by US Department of Defense (DoD), the RMF is currently maintained by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The main objective of RMF is to improve the information security and risk management process. CAP holders are considered experts in RMF with the ability to structuring the processes for risk assessment and establishing security documentations.
CAP Fast Facts
- Introduced in 2005
- More than 140,000 CAP certified professionals
- Developed and Approved by US Department of Defense (DoD)
- The only certification under DoD8570 mandate that aligns with RMF steps
Who Should Earn CAP
CAP is an ideal certification for people working in Information Security (IS), Information Technology (IT), and Information Assurance (IA) fields. CAP holders can acquire or work on the following key positions in the organizations.
- IS Manager
- IS specialist
- IT Auditor
- IT Manager
- Cyber-security analyst
- Cyber-security engineer
The professionals who use the RMF in the following departments/areas can also acquire CAP certification to prove their dominance in the respective fields.
- Local governments
- Civilian roles
- Private Sector organizations
- Military
- Federal government departments, such as US Department of Defense (DoD)
CAP Exam
The following exam criterion is set for the professionals interested in CAP certification.
| Exam Particulars | Details |
| Exam Language | English |
| Total Questions | 125 |
| Questions Format | Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |
| Exam Score | 1,000 Points |
| Passing Score | 700 Points |
| Exam Duration | 3 Hours |
| Exam Centers | Pearson VUE |
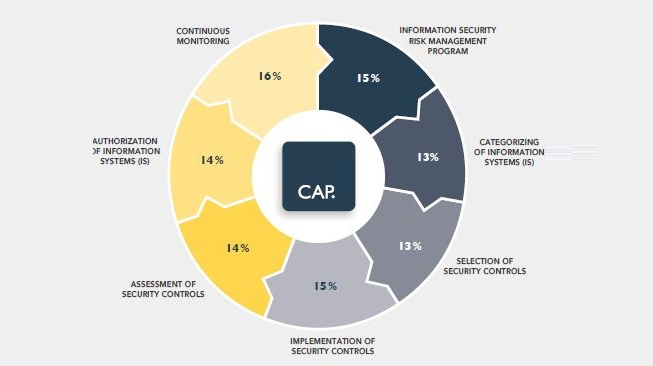
CAP exam is based on the questions from the following 7 domains.
| Domain | Exam Weight |
| Continuous Monitoring | 16% |
| Information Security Risk Management Program | 15% |
| Implementation of Security Controls | 15% |
| Assessment of Security Controls | 14% |
| Authorization of Information Systems | 14% |
| Categorization of Information Systems | 13% |
| Selection of Security Controls | 13% |
| Total Domains = 07 | Total Percentage= 100% |
Eligibility Criteria
The candidates interested in CAP must have a minimum of 2 years of cumulative work experience in one or more of the aforementioned CAP domains. Candidates with no prior work experience can also take the CAP exam. In the latter case, the successful candidates are entitled as Associate of (ISC)2 and given 3 years of time to gain the experience required to earn the CAP certification.
CAP Domains Overview
(ISC)2 evaluates the competence of the candidates in the following domains. The candidates interested in CAP certification must have the information and understanding of these domains to get certified.
Domain 1: Information Security Risk Management Program
- Understanding the information security risk management programs at organizational level. This includes
- information security principles
- Risk Management Framework (RMF) managed by NIST
- Integration of RMF with System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Boundary requirement for Information System
- Security control knowledge
- Authorization role and responsibilities
- Understanding risk management program processes covering the following
- Privacy requirement information
- Program management controls at enterprise level
- Information System hosted by third-parties
- Knowledge of regulatory and legal requirements including the following.
- Knowledge of information about federal information security
- Privacy legislation and security-related mandates
Domain 2: Categorization of Information Systems (IS)
- Knowledge of Information System
- Knowledge of Information System architecture
- Ability to identify the boundaries of Information System
- Understanding of purpose and functionality of Information System
- Categorizing the Information System
- Identifying the information that is stored, transmitted, or processed by the Information System
- Determining the impact level for different types of information. The impact level is determined on Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA)
Domain 3: Selection of Security Controls
- Identification and documentation of inherited and standard controls
- Selection of security controls
- Determining and documenting the applicability of recommended controls
- Developing strategies for monitoring the security controls
- Assessment and approval of security plans
Domain 4: Implementation of Security Controls
- Implementation of selected security controls
- Aligning the security controls with the organizational architecture
- Determining the mandatory configuration and verifying the implementation according to the standards, such as NIST, Security Technical Information Guides (STIGs), and United States Government Configuration Baseline (USGCB)
- Documenting the implementation of security controls
- Documenting the input, output, and expected behavior of security controls
- Analyzing the input, output, and expected behavior of security controls to ensure their alignment with impact and scope of Information System
- Obtaining the information regarding the implementation of security controls from the respective entities
Domain 5: Assessment of Security Controls
- Preparing for security controls assessment
- Determining the requirements for Security Control Assessor (SCA)
- Establishing the scope and goal of assessment
- Determining the required methods and level of assessment
- Determining the resources and logistics required to carry-out the assessment
- Analyzing previous assessments and other documents that can aid in carrying out the assessment
- Finalizing the assessment plan
- Conducting the Security Control Assessment
- Running the assessment plan according to the standard assessment methods
- Documenting the findings of security controls assessment
- Preparing the preliminary Security Assessment Report (SAR)
- Identifying the weaknesses in security controls by analyzing the assessment results
- Proposing the remediation for the discovered weaknesses in the assessment
- Taking action based on the proposed remediation.
- Developing the final SAR
Domain 6: Authorization of Information Systems
- Developing action plan and milestones
- Analyzing the risk in security controls
- Prioritizing the risk response based on risk level
- Identifying the resources for remediation plans
- Deploying or scheduling the remediation plans
- Compiling the security documents required for authorization of security officials
- Evaluating the Information System risk and appropriate plan (whether to avoid, mitigate, transfer, share, or accept the risk)
- Determining the terms for security authorization decision
Domain 7: Continuous Monitoring
- Determining the impact on security due to proposed changes to Information System
- Assessing the deployed security controls based on the devised strategies
- Assessing, formulating, and conducting the remediation tasks according to the discovered vulnerabilities or weaknesses
- Reporting the security status and updating all the documents
CAP Renewal Policy
CAP certification is valid for three years. Recertification is required after every three years to maintain the credential. Recertification through Continuing Professional Education (CPE) can be accomplished by submitting 60 CPE credits over a period of three years. (ISC)2 offers different opportunities like webinars, read and write assignments, and events to earn CPE credits.

