Galileo is an open source web application auditing tool capable of performing various penetration tests, such as information disclosure, fingerprinting, bruteforcing, injection attacks, shellshock exploitation, and ASP.NET scanner tests. Galileo uses the following inbuilt modules to perform these tasks.
Disclosure
Bruteforce
Fingerprint
Injection
Exploits
Scanner
Disclosure modules are used to gather information like credit card data, private IPs, application’s source code, and email addresses linked with the target web application. Bruteforce modules perform bruteforce attacks to find out credentials, backup data, directories, and hidden files on the web server. Fingerprinting modules are used to gain the Content Management System (CMS), framework, and server information. The injection modules simulate OS command and SQL injection attacks to see if the target web application is vulnerable to the said attacks. The exploits modules search for the vulnerabilities related to the source code of the target web application. The scanner modules look for ASP.NET vulnerabilities in the target web application. Apart from these tasks, Galileo can perform functions like URL encoding, creating hash strings, and invoking external tools.
Galileo Installation
Galileo is a Linux tool that requires Python version 2 to operate. In order to use Galielo, clone the tool using the following path.
git clone https://github.com/m4ll0k/Galileo.git galileo
Navigate to the tool’s directory to install the missing dependencies using the following commands.
cd galileo python2 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
How Galileo Operates
Type the following command in the terminal to execute Galileo tool.
Python2 galileo.py
The help command shows all the available parameters and options required to operate Galileo tool.
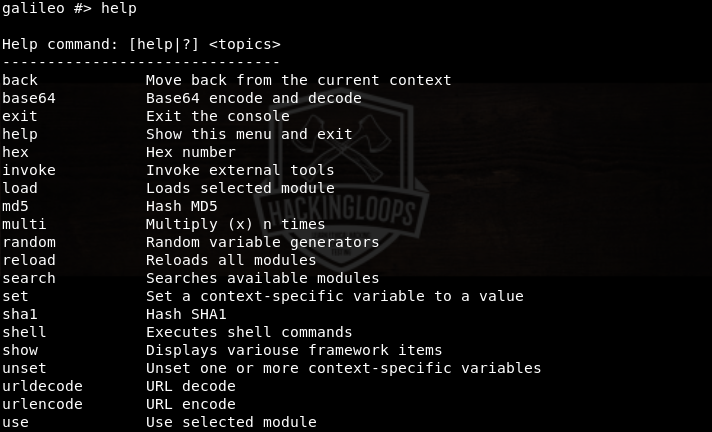
Among these, show, use, set, and run are the most frequently used parameters. For example, we use the show parameter to see all the available modules using the following command.
show modules
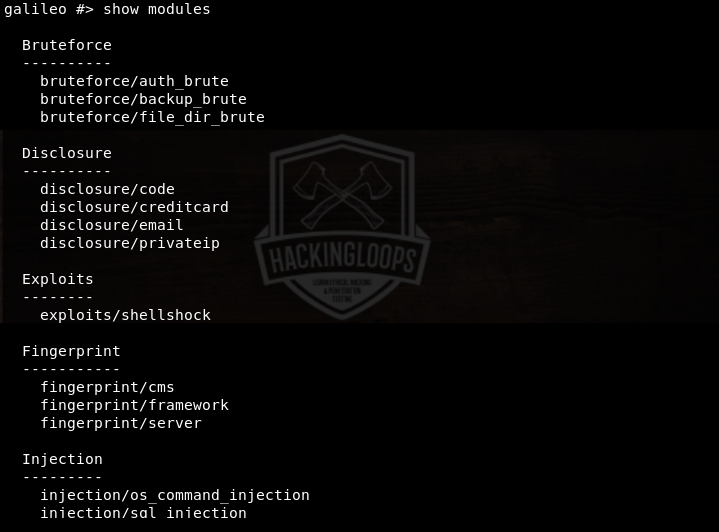
The show options command is used to see the mandatory and optional values required to run each module. The use parameter is used to select the desired Galileo’s module. For instance, we can select the sql injection module as follows.
use injection/sql_injection
Type the following command to see all the mandatory and optional values required to launch the SQL attack on the target web application.
show options
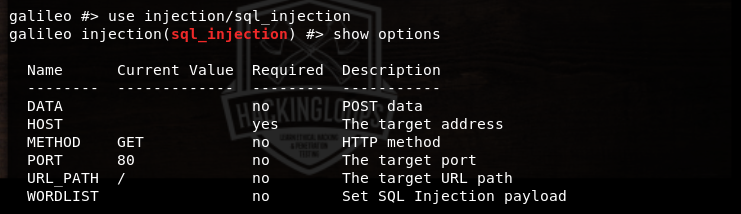
The above screenshot shows that the HOST value is mandatory to launch the SQL injection attack. All other values are optional. We can use the set parameter to define the target web host application (e.g testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=3) in the following manner.
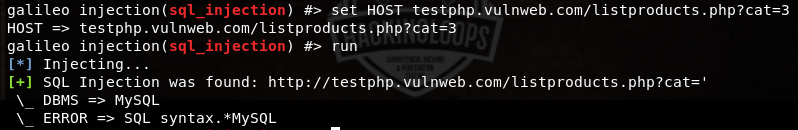
set HOST testphp.vulnweb.com/listproducts.php?cat=3
The run command executes the SQL injection module to see if the target web application is vulnerable.
run
If the target web application is vulnerable, Galileo shows the backend database management system and error information as shown in the following screenshot.
All other modules available in the tool can be used using similar commands. As mentioned above, Galileo can perform various other tasks like url encoding and decoding, hash generation, producing random numbers, and invoking external tools. For instance, we can invoke nmap tool to test specific port and host status using the following command.
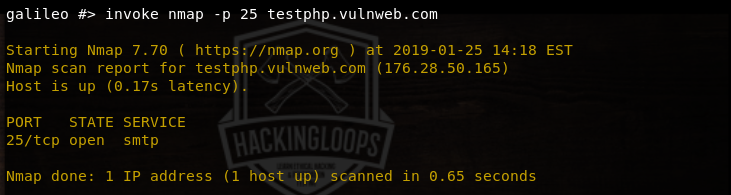
invoke nmap –p 25 testphp.vulnweb.com
The –p flag represents the port, 25 is the port number, and testphp.vulnweb.com is the target web application. The tool fetches results about the status of the target host and port number in the following format.
Conclusion
Galileo is a lightweight penetration testing tool that can check various security flaws in web applications including the critical database vulnerabilities.

Leave a Reply